Intracranial Pressure Monitoring Devices—a recent breakthrough— assess and evaluate the intracranial pressure by being induced in an afflicted patient who is encountering an erratic ICP level. These are being ubiquitously used for trauma patients with severe head injuries, subarachnoid haemorrhage, large strokes, or structural lesions.
ICP monitoring is deemed extremely pivotal for the administration of severe brain injury because the cranium encloses the brain and if there’s any shift in the space of this encompassing container, an elevation in the ICP can be caused. Thus, ICP monitoring devices serve as an indispensable aid in formulating treatments for brain-trauma patients.
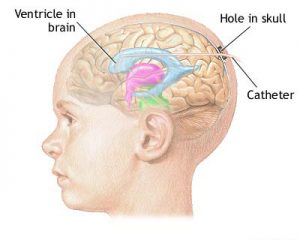 ICP monitors are largely segregated into two classifications: Those which only prodder ICP data, colloquially referred to as “bolt”, and those which facilitate concurrent drainage of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) while evaluating the ICP.
ICP monitors are largely segregated into two classifications: Those which only prodder ICP data, colloquially referred to as “bolt”, and those which facilitate concurrent drainage of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) while evaluating the ICP.
Monitors that detect changes in pressure based on flow through a fluid-filled system are most accurate when the system is closed to drainage. The combination of a ventriculostomy with a closed drainage system is also known as an external ventricular drain (EVD). Bolts commonly use fibre-optic technology that allows for continuous ICP monitoring without CSF drainage.
There’s a variegated spectrum of products available today for efficaciously carrying out the functions of the Intracranial Pressure Monitoring Device. These include:
Integra Neuroscience Products
The Integra Neuroscience external drainage catheter is a CSF diversion device that is instrumental in evaluating ICP. The catheter tubing is translucent with depth markings and contains a radio-opaque barium sulfite strip. ICP readings are based on a fluid-filled transduction system that transmits changes in ICP through a saline-filled tube to a diaphragm on a strain gauge transducer. This monitor must be levelled with the Foreman of Monro (approximately the level of the external auditory canal) after insertion and should be zero-balanced daily. The level of the drain can be adjusted to allow more or less CSF drainage.
Codman Products
The Codman Microsensor catheter can be used as an intra-parenchymal or intra-ventricular monitor depending on the depth of the catheter. Different drill bits are used to allow for variable depths of measurement. If used as an intra-ventricular monitor, the catheter will also allow for CSF drainage. This system uses a fibre-optic transducer that must be zero-balanced prior to insertion. The Codman ICP monitor uses a micro-miniature strain gauge located at the tip of the monitor that transmits changes in pressure over a diaphragm. Changes in electrical resistance are reflected on an external monitor.
Gaeltec Products
The ICT/B pressure sensor is intended to monitor ICP subdurally. It contains a balloon-covered pressure sensor that is activated when filled with air. This monitor is self–zero-balanced in vivo and is reusable.